
on Posted on Reading Time: 4 minutes
The wholesale telecoms space is undergoing a period of rapid transformation. Facing competition from hyperscale cloud providers and digital startups who have been able to deliver a new breed of fast, reliable, and secure on-demand services to enterprise customers at unbelievably attractive prices, traditional communications service providers (CSPs) are in a race to build new digital capabilities.
In this race, CSPs need to embrace disruptive innovation, and take advantage of 5G, IoT and edge compute technologies.
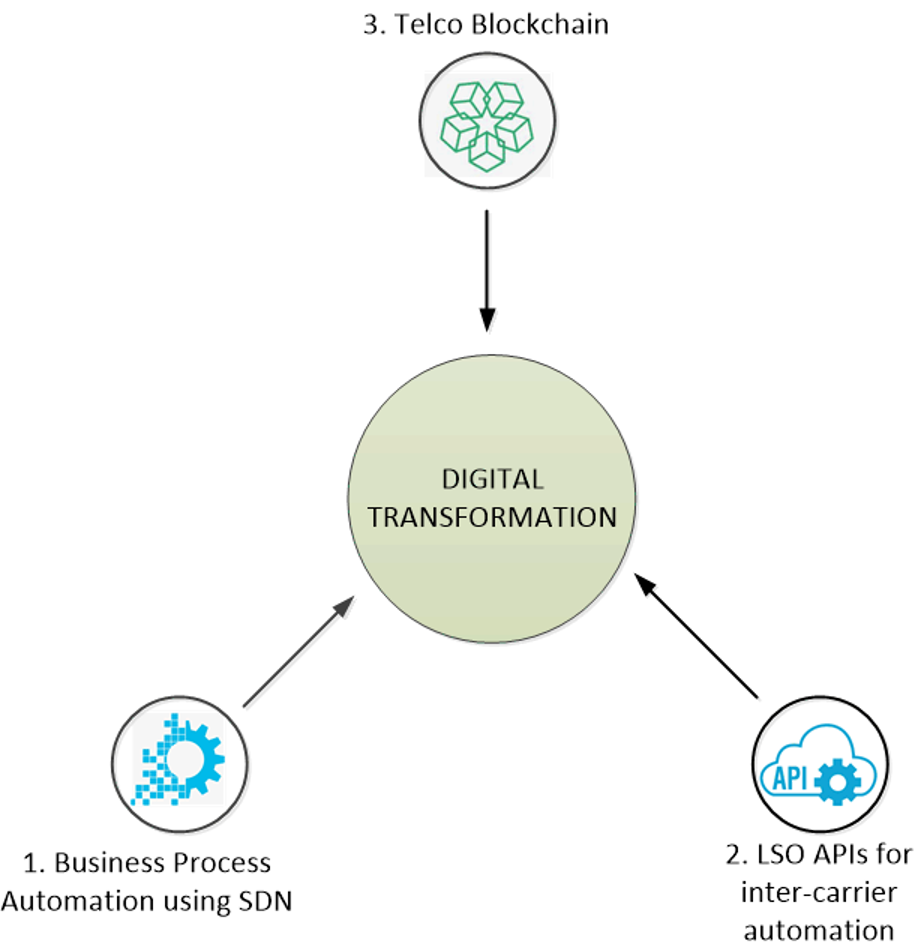
Most traditional CSPs still rely on manual business processes. In order to transform and compete in the market with newer products and service offerings, they need to adopt automation in the following 3 ways:
1. Business Process Automation (BPA) using SDN
The first building block for CSPs embarking on their automation journey is to deploy a digital core that ensures no manual workflows stand in the way of their service delivery. This requires complete automation of the MEF Lifecycle Service Orchestration (LSO) cycle which includes online order acceptance, automated service provisioning, service delivery, and ticketing.
2. LSO APIs for inter-carrier automation
Next, CSPs need to leverage the standards-based LSO APIs to enable end-to-end orchestration of these services across multiple service provider networks. MEF has created a framework for automating the lifecycle of a connectivity service from end-to-end across multiple networks, covering many business functions, such as address validation, site query, product offering qualification, product inventory, billing and invoicing, and much more.
3. Blockchain technology for inter-carrier settlement
Finally, CSPs need to adopt blockchain technology for automated billing and settlement of all their inter-carrier sales transactions, which are critical to offering on-demand services (more about that later).
Diagram 1: The Three Stages of Carrier Automation
The Move to NaaS is Underway
There are several thousand CSPs worldwide which operate in an environment of “co-opetition,” by this I mean they compete in their efforts to capture a greater market share but also cooperate with each other, as no single service provider can cover all geographies.
In order to deliver an end-to-end service to enterprise customers, CSPs must work together to deliver backend integration and automation of systems and processes for quote, orders, billing, and settlement.
Today, the inter-carrier invoice settlement and reconciliation process is manual and typically takes between 45 and 60 days per order. This process is highly inefficient, and this problem is further exasperated with the advent of new 5G and IoT services.
With millions of new devices being connected to networks, CSPs need a more flexible and faster way to on-board and manage these new volumes of network traffic.
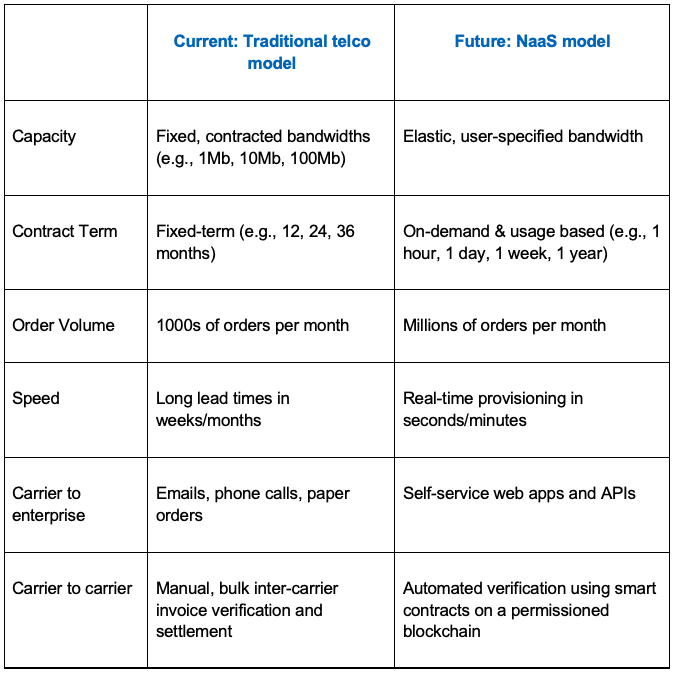
The move to a Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) model achieves this speed and flexibility in a number of different ways, as highlighted in the following table:
Smart Contracts Will Lead the Way to a Smarter Future
On the settlement side, blockchain technology offers vast potential for CSPs. Use of a permissioned blockchain-based solution can dramatically cut down settlement times, as well as significantly improve the verification process for transactions.
With an automated solution that uses a smart contract, each order and its billable attributes are recorded on a distributed ledger that is made accessible to any participating CSP. This eliminates the manual paper verification process and reduces settlement times from several months to an instance.
The success of this type of automated billing and settlement solution hinges on industry-wide collaboration. There are three steps that CSPs can take to get going with blockchain technology:
- Step 1: Tokenization of their network ports, end-devices, and IoT devices
- Step 2: Enable online-only orders for their services using web portals and/or APIs, which are captured on a blockchain network
- Step 3: Introduce smart contracts to trigger an inter-carrier settlement process based upon record on the blockchain
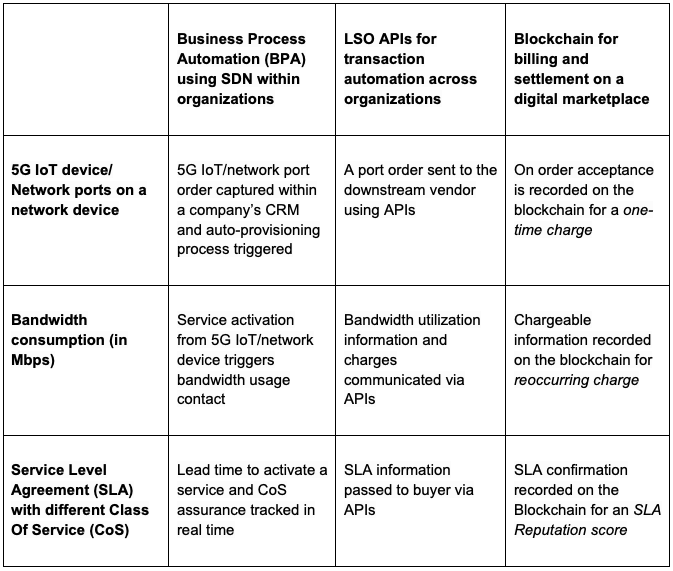
The table below explores some of the CSP use cases for blockchain technology:
Success of Automation Relies on Industry Collaboration
Automation not only has the potential to eliminate several major pain points for CSPs, but also drives innovation.
For example, a blockchain-based solution for inter-carrier payment settlement will enable CSPs to tap into new opportunities with 5G and IoT, which previously might not have been viable given the low cost per connected device.
The ability to access these types of services on-demand through a pay-as-you-go model will be extremely attractive to enterprise customers and will ultimately help them lower operational costs (during a period when most face rising costs).
The move to NaaS presents an opportunity for CSPs to recapture some of the market share from hyperscale cloud providers and digital startups. With the NaaS market expected to grow from over $11 billion in 2022 to over $80 billion by 2029, CSPs need to act fast.
Although introducing automation to your internal business processes is a good first step, it will only get you so far.
In order to accelerate telco transformation and deliver innovative on-demand services, the industry needs to work closely together on the adoption of LSO APIs and blockchain technology, which are crucial for delivering truly end-to-end automation.
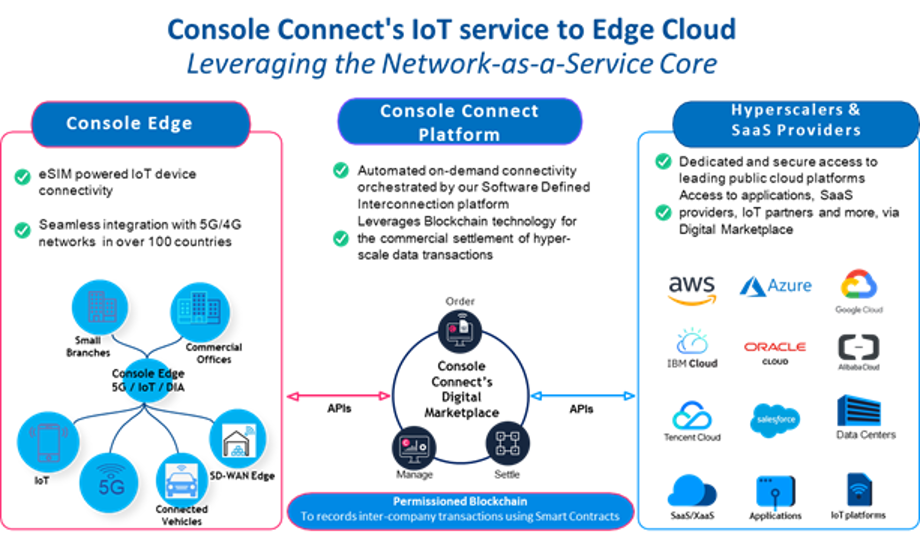
Diagram 2: Console Connect’s Automation Journey
Learn More
Learn more about MEF LSO APIs.
Learn about Console Connect.

